Contents:
Biometric data used as a personal security token proved to be a reliable way for protecting our devices from unwanted eyes. But scaled to the enterprise level, biometric authentication can be a robust security tool that simplifies access to sensitive data, and set restriction levels that are easy to manage.
Since 2019, MobiDev has been developing and improving an office security system based on biometric data of our staff, as well as using biometric authentication in our client’s applications. So in this article, we’ll discuss the basics of biometric authentication, verification, and identification in 2024, and how it changed with the implementation of AI based on our own experience.
Biometrics Technology Overview
At its core, the objective of biometric security technology is to improve security using parts of our bodies that cannot be easily replicated. This includes fingerprints, face shape, iris, our voice timbre, or even gate manor. Although machine learning and quantum computing may be able to guess a password, biometric information like fingerprints, faces, and irises are not so easily determined or emulated.
Authentication with biometric data can be implemented to access any physical or digital property, which proposes much easier access since a biometric security token is always with you, can’t be lost, or easily replicated. Another important aspect is that our biometric prints don’t change much over time, which allows us to collect data just once.
In case you are trying to elaborate on the requirements for your biometric software, or struggle to conduct a technical audit of your platform, MobiDev can handle this for you. We offer AI consulting service that includes concise analysis of your existing infrastructure, creating development strategy and ensuring data compliances are implemented. Just book a call with my team and we’ll help you to create an optimal solution for biometric authentication.
STUCK WITH BIOMETRIC SECURITY?
We'll provide you with concise answers and documentation for developing biometric authentication solution
Get in touchTypes of Biometrics
Biometrics technology can be split into three domains: identification, verification, and authentication.
- Identification is used when the system wants to know who the user is.
- Verification is about using that biometric information to determine if any other information is associated with the user.
- Authentication is to understand if the identity the user claims to be is correct and authorized to access the services and data they are requesting.
An example of biometric identification may be used to determine the identity of a user against a database of faces. Law enforcement facial recognition databases use this technology to a great degree and can help investigate security camera evidence footage with better accuracy than a human.
Verification is helpful for ensuring that the user and the information stored in the database about them match. Authentication is perhaps the most critical of the three, enabling authorized users to access sensitive information while restricting unauthorized persons.
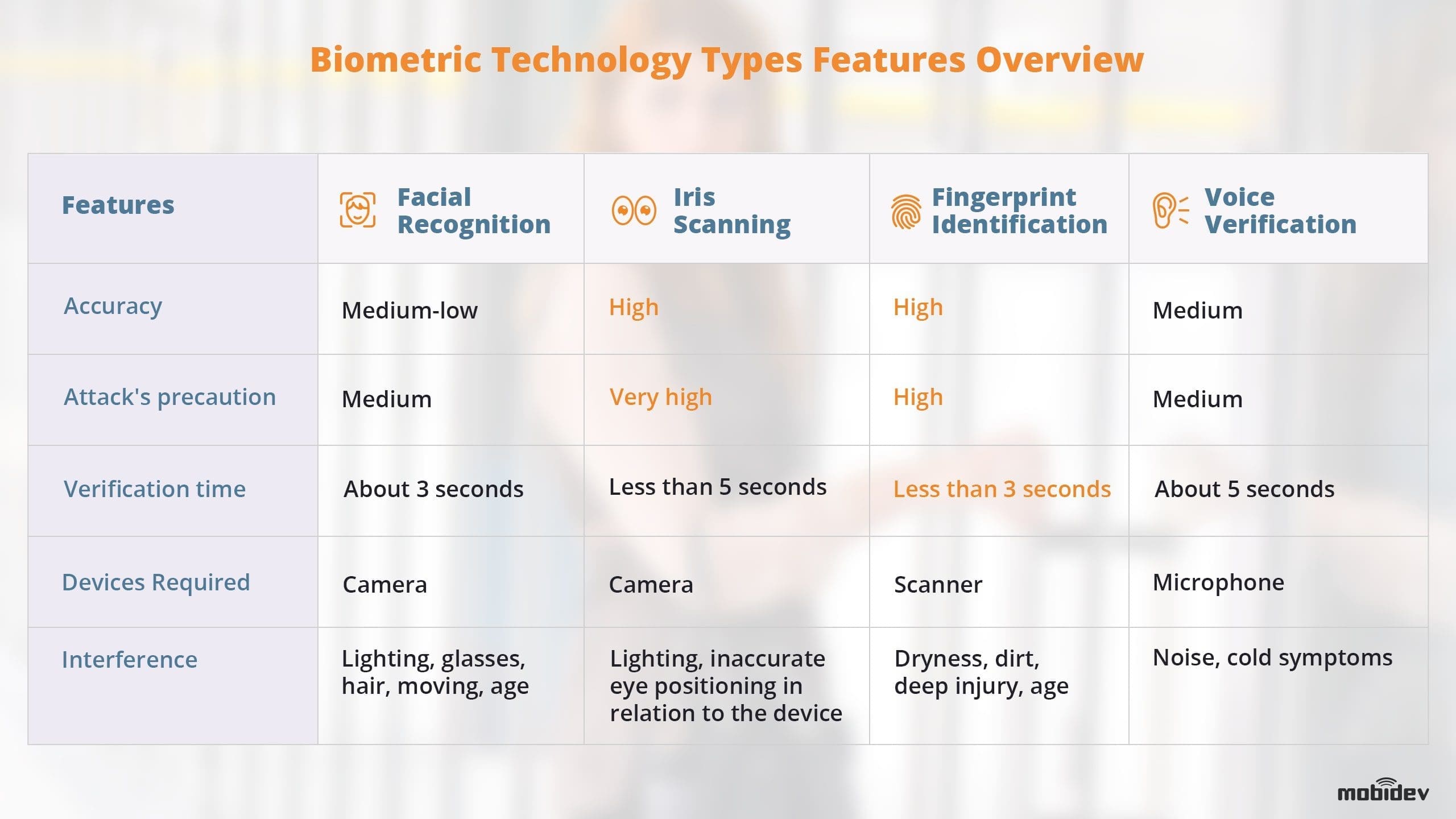
The table below shows the various characteristics of each type of biometric technology.
One of the most important takeaways for any business considering biometric security methods is that it is not always wise to rely on only one form of biometric technology, i.e. unimodal. Instead, a multimodal approach that uses more than one type of biometrics is much more secure. So now, let’s talk about specific types of biometric data that can be used for all three types of security software.
Facial Recognition Technology
Face recognition methods imply using eigenfaces to differentiate between people’s images. However, modern approaches rely on distinctive features of the faces in relation to other elements of the human face and their location. We have a dedicated article on facial recognition technology, so if you want an in-depth look at how it works and what approaches are used today, check it.
One of the reasons why facial recognition technology has significantly improved the quality of recognition, is the usage of face masks during pandemic. Many facial recognition solutions now take into account existing obstacles like face coverings, dense shades, etc. Since 3D cameras can get much more information about a human face than a two dimensional camera would, facial recognition is much more secure than before as a biometric authentication technology.
Previously, it was much easier for computers to be fooled by a picture of someone’s face or a similar looking face. However, machine learning has helped narrow the margin of error to prevent hackers from exploiting facial recognition-based security and various anti-spoofing methods now exist.
Voice Recognition Technology
Voice recognition has tons of applications in authentication and verification. Being able to identify someone and verify their access based on their voice can save a lot of time, but we are getting to the point where voices may not be as secure as other biometric methods. Deep learning has made it possible to realistically mimic a voice using a computer, a technique called vocal synthesis. ‘Deep fake’ voices have been used in successful fraudulent activity that in one case cost an energy firm in the United Kingdom $250,000 in 2019.
We solved this problem in our own practice by developing a biometric office security system that uses face identification combined with voice verification. But, to avoid being tricked with deep fake technologies, we also used various text-to-speech anti-spoofing methods to make it more secure. This project relies on an edge device, Jetson Xavier that provides faster processing power and ensures all the data is stored closer to the user and the whole system can operate in case of energy shortages.

Read also:
Using Edge Biometrics For Office SecurityAs deep learning technology improves, the more realistic vocal synthesis will become. Unless technology improves to better recognize legitimate vs fake voices, voice recognition biometrics technology is better suited for non-security applications, particularly identification. This may be for consumer based systems like smart homes, or enterprise solutions such as automatic transcriptions of meeting recordings that can attribute speakers by name.
Iris Scanning Technology
This form of biometrics technology is one often seen in science fiction. It is similar to facial recognition in that it is contactless, but focuses only on one particular feature, the eye. One advantage is that there is less complexity to account for. Advanced facial recognition systems are not needed, only something that can recognize the features of the iris. You don’t necessarily have to be close to an eye to scan the iris. At 40 feet away, tests at Carnegie Mellon University can scan an iris.
One advantage of this technology is that because it uses infrared sensors to analyze the iris, scanning the eye can be done in low light conditions.
Law enforcement applications of this technology for identification of suspects is definitely one of the first things that may come to mind.
Fingerprints Authentication Technology
Everybody knows how Touch ID works, since we use fingerprint authentication everyday on our smartphones and laptops. By comparing grooves and valleys of an individual’s finger against a standard subject or a set of subjects, a person can be identified or verified in any system that has proper sensors for scanning fingerprints.
One downside of this method is that it requires finger scanning hardware that’s not widely used as for example web or smartphone cameras. But fingerprint scanning turns out to be faster and more reliable that for example face recognition, because it only requires a touch.
How AI Can Improve Biometric Authentication Systems
When it comes to security, improving accuracy and efficiency of biometric authentication systems cannot always be done with human programming. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can help us make our systems more secure and efficient.
Biometric technologies can be split into two domains, physical and behavioral.
Physical Biometric Technology
Physical biometrics include everything that we have already discussed in this article. These are objective characteristics of a person like their face or fingerprints, DNA, and more. This must be converted into data that can be analyzed by the AI system and compared against a database for authentication purposes.
One of the cases where AI and ML prove most helpful is with facial recognition. Used extensively with augmented reality solutions, AI can help make facial recognition by computers much easier by analyzing facial features and matching them with a database.
Behavioral Biometric Technology
One of the most interesting trends that artificial intelligence makes possible is behavioral biometric technology. This uses unique behavioral characteristics of how they interact with the world, things that the user may not even realize about themselves. This is one of the most effective lines of defense against deep fake fraud attempts. Some of the more popular ways to measure behavioral biometrics are:
- Mouse activity
- Keystroke movement
- Touch screen press size, area, and pressure
- Mobile device motion
The Biometrics and Data Pattern Analytics Lab from the Autonomous University of Madrid developed BeCAPTCHA, a system for bot detection that uses behavioral biometrics. It’s entirely possible that behavioral biometrics can be used without the user’s knowledge, eliminating the need for annoying tests of the user’s humanity as CAPTCHA challenges have done for years. In the next few years, users may never have to click on pictures of crosswalks and stop lights to prove they are ‘not a robot’ again while browsing the Internet.
Importantly, behavioral biometrics can assist in ensuring security throughout an entire session. For example, if a user authenticates themselves and then leaves the room, unwittingly enabling an unauthorized user to gain access to their computer, this would be a serious security risk. However, behavioral biometrics can detect the inconsistent behavior of the second user and restrict their access dynamically.
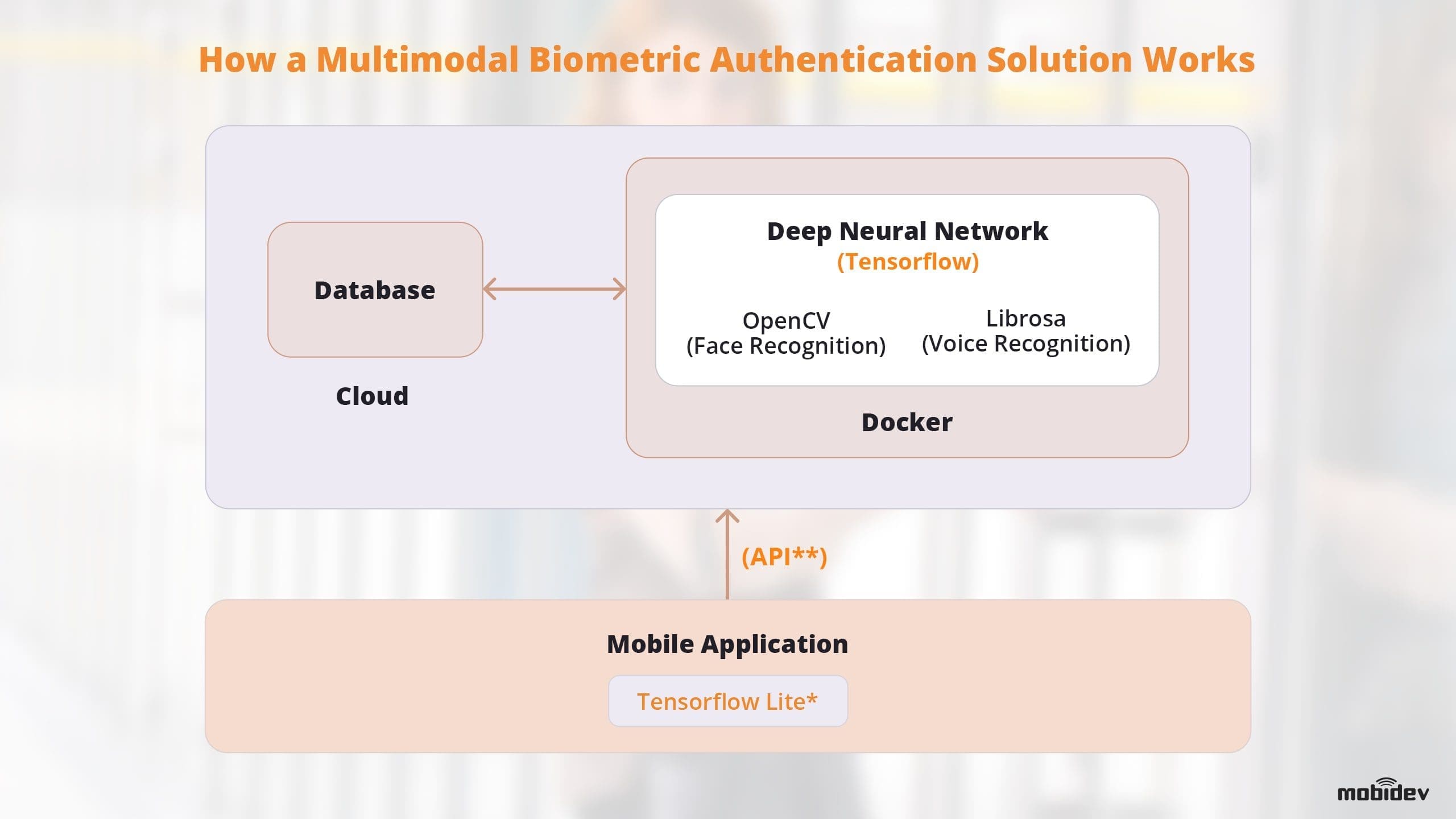
How Multimodal Biometric Authentication Solutions Work
Every form of biometrics technology has pros and cons. They each are also not universally effective. To improve accuracy and effectiveness of biometric authentication technology, it’s important to layer security with multimodal biometric recognition solutions. We can see this in action in the following diagram:
* Neural networks on mobile applications can be challenging to develop and implement. Neural networks can be integrated into applications using TensorFlow Lite, however there are various limitations. Training your neural network models with the TensorFlow library can help. You will need to thoughtfully design the architecture of the application beforehand and put those requirements into consideration.
** If a native application is not possible, this process can be offloaded to the cloud to process the data like Rest API. However, this will incur additional networking resources and require an Internet connection.
There is an Nvidia Docker that can simplify the deployment of the system, while a service provider (such as AWS) can provide an uninterrupted communication channel, computing power for neural networks, and a convenient interface for scaling your system.
Test #1: Facial Recognition
The user creates a photo-imprint that’s stored on the device using a camera. This biometric imprint is converted and normalized using the OpenCV library.
The face is identified using a photo, and each of the 64 landmarks detected by OpenCV are highlighted. A biometric verification landmark includes things like a distance from the bridge of the nose to the eye and other facial features.
These landmarks and a cutout image of the face are transferred to a deep neural network, which is trained using the TensorFlow library.
An eDNA feature vector is formed after neural network processing is completed. The feature vector collects the biometric characteristics of a particular person. The length of the vector is usually 2048 bits. The lengths depend on the DNN architecture.
During verification, eDNA is issued and compared with the anchor record that was formed earlier. Reverse engineering is impossible because there is no access to the vector. The biometric system will periodically update this anchor record to match an individual’s changing looks.
Test #2: Voice Verification
The user provides a voice sample through a microphone that gets processed by the Librosa library. The library reads the audio, transforms and converts it, and then transmits biometrics to the neural network (DNN).
An eDNA feature vector (2048 bits) is formed, which takes into account such biometrics as timbre, intonation, tempo, pitch, and other characteristics that the neural network was trained to respond to.
Success Story: AI-based Biometric Authentication Solution
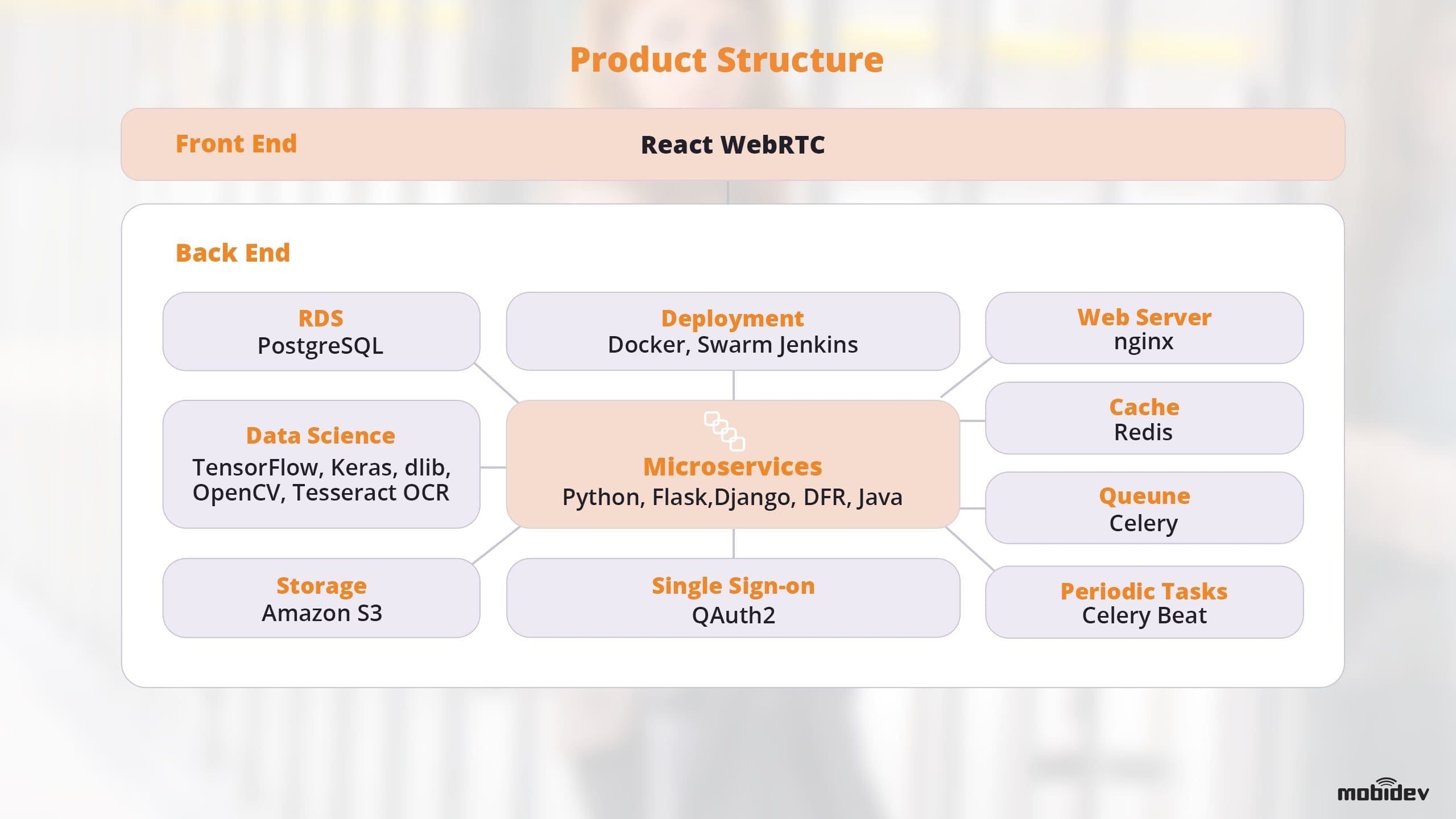
By combining a microservice-based architecture, WebRTC, and machine learning powered biometric recognition, we developed a single sign-on (SSO) biometric authentication solution for a US-based firm. Utilizing voice and facial recognition, we developed an enterprise verification as-a-service (EVaas) solution that uses the technologies and trends discussed earlier.
This product proved that biometric authentication systems can be highly customizable and easy to use, powering a very simple user interface from behind the scenes. In addition, this example was able to integrate with existing systems via API.
Face & Voice Authentication Solution
Read Success StoryBiometric Authentication Solutions Development
Security systems contain a lot of pitfalls when it comes to using biometric data, since you need to take in account database security as serious as the subject of biometric authentication. One of the ways to ensure all the privacy compliances are implemented in your software, and there are no data breaches that can lead to leakage of biometric information and lawsuits.
Our AI consulting service units seasoned engineers with the average 5+ years of experience in specific technologies like biometrics. We make sure the client receives all the required artifacts during the consultancy stage and support their teams with our engineering resources through the development. If you already investigate what’s the best approach to building a biometric security system, fill out the contact form and get in touch with the MobiDev team.